使用 PyTorch 和 TIAToolbox 进行全切片图像分类
为了充分利用本教程,我们建议使用此 Colab 版本。这将使您能够尝试下面提供的信息。
简介
在本教程中,我们将展示如何借助 TIAToolbox 使用 PyTorch 深度学习模型对整个切片图像(WSIs)进行分类。WSI 是通过手术或活检获取的人类组织样本的图像,并使用专门的扫描仪进行扫描。病理学家和计算病理学研究人员使用这些图像来在微观水平上研究癌症等疾病,以便了解例如肿瘤的生长情况,并帮助改善患者的治疗方案。
处理WSI(全切片图像)之所以具有挑战性,主要在于它们的巨大尺寸。例如,一张典型的切片图像大约有100,000x100,000像素,其中每个像素可能对应切片上约0.25x0.25微米的区域。这带来了加载和处理此类图像的挑战,更不用说在一项研究中可能要处理数百甚至数千张WSI(规模越大的研究通常能得出更好的结果)!
传统的图像处理流程并不适用于WSI处理,因此我们需要更好的工具。这就是TIAToolbox发挥作用的地方,它提供了一套实用的工具,能够以快速且计算高效的方式导入和处理组织切片。通常,WSI以金字塔结构保存,其中包含同一图像在不同放大倍数下的多个副本,这些副本为可视化进行了优化。金字塔的第0层(或底层)包含最高放大倍数的图像,而金字塔的较高层级则包含较低分辨率的图像副本。下图展示了金字塔结构的示意图。
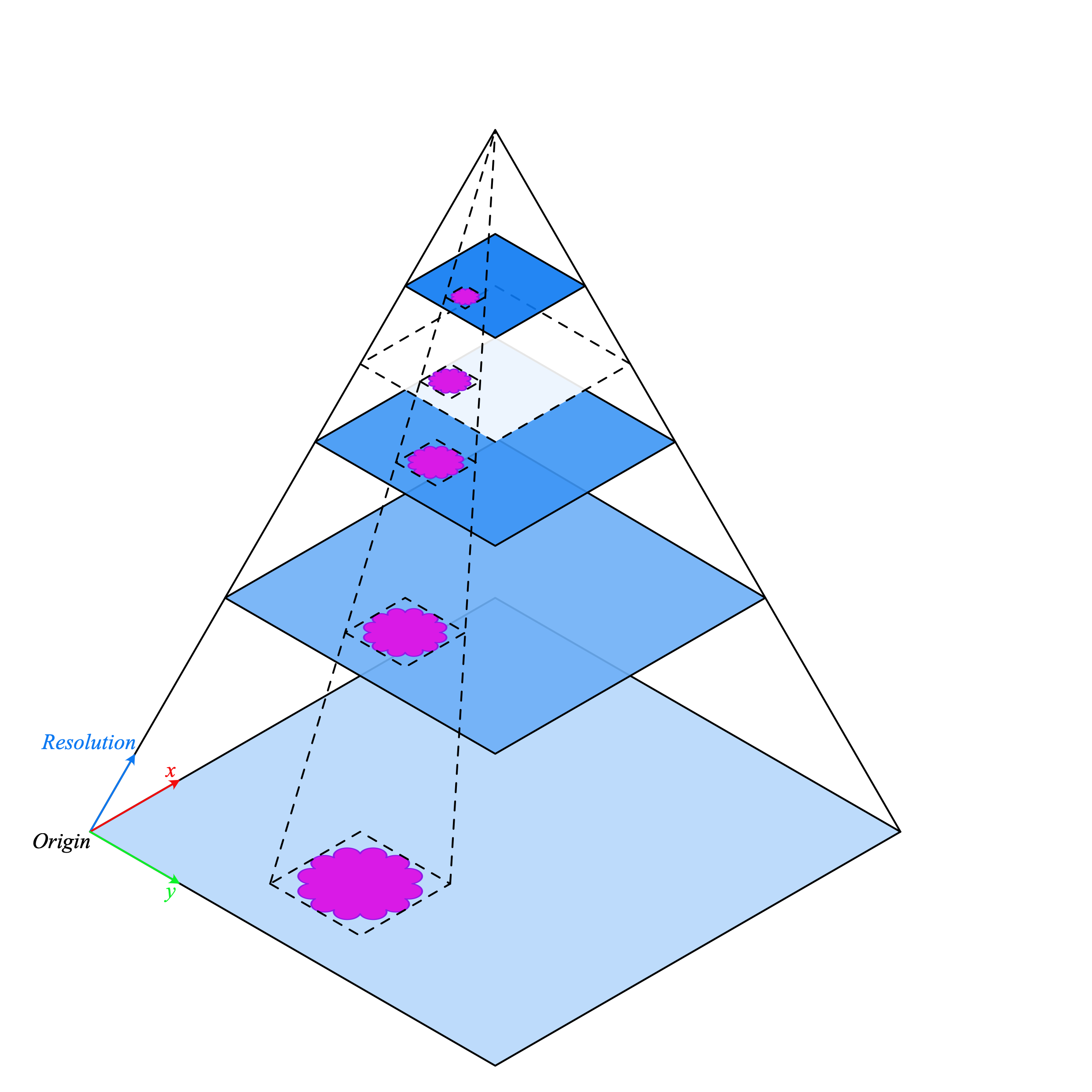 WSI 金字塔堆栈 (来源)
WSI 金字塔堆栈 (来源)
TIAToolbox 使我们能够自动化常见的下游分析任务,例如组织分类。在本教程中,我们将展示如何:1. 使用 TIAToolbox 加载 WSI 图像;2. 使用不同的 PyTorch 模型在 patch 级别对切片进行分类。在本教程中,我们将提供一个使用 TorchVision ResNet18 模型和自定义 HistoEncoder <https://github.com/jopo666/HistoEncoder>`__ 模型的示例。
让我们开始吧!
环境设置
要运行本教程中提供的示例,以下软件包是必需的先决条件。
-
OpenJpeg
-
OpenSlide
-
Pixman
-
TIAToolbox
-
HistoEncoder(用于自定义模型示例)
请在终端中运行以下命令以安装这些包:
apt-get -y -qq install libopenjp2-7-dev libopenjp2-tools openslide-tools libpixman-1-dev pip install -q ‘tiatoolbox<1.5’ histoencoder && echo “安装已完成。”
或者,您可以在 macOS 上运行 brew install openjpeg openslide 来安装所需的包,而不是使用 apt-get。更多安装信息可以在这里找到。
导入相关库
"""Import modules required to run the Jupyter notebook."""
from__future__import annotations
# Configure logging
importlogging
importwarnings
if logging.getLogger().hasHandlers():
logging.getLogger().handlers.clear()
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore", message=".*The 'nopython' keyword.*")
# Downloading data and files
importshutil
frompathlibimport Path
fromzipfileimport ZipFile
# Data processing and visualization
importmatplotlibasmpl
importmatplotlib.pyplotasplt
importnumpyasnp
importpandasaspd
frommatplotlibimport cm
importPIL
importcontextlib
importio
fromsklearn.metricsimport accuracy_score, confusion_matrix
# TIAToolbox for WSI loading and processing
fromtiatoolboximport logger
fromtiatoolbox.models.architectureimport vanilla
fromtiatoolbox.models.engine.patch_predictorimport (
IOPatchPredictorConfig,
PatchPredictor,
)
fromtiatoolbox.utils.miscimport download_data, grab_files_from_dir
fromtiatoolbox.utils.visualizationimport overlay_prediction_mask
fromtiatoolbox.wsicore.wsireaderimport WSIReader
# Torch-related
importtorch
fromtorchvisionimport transforms
# Configure plotting
mpl.rcParams["figure.dpi"] = 160 # for high resolution figure in notebook
mpl.rcParams["figure.facecolor"] = "white" # To make sure text is visible in dark mode
# If you are not using GPU, change ON_GPU to False
ON_GPU = True
# Function to suppress console output for overly verbose code blocks
defsuppress_console_output():
return contextlib.redirect_stderr(io.StringIO())
运行前的清理工作
为确保正确清理(例如在异常终止时),所有在此次运行中下载或创建的文件都保存在一个单独的目录 global_save_dir 中,我们将其设置为“./tmp/”。为了简化维护,该目录名称仅在此处出现一次,以便在需要时可以轻松更改。
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
global_save_dir = Path("./tmp/")
defrmdir(dir_path: str | Path) -> None:
"""Helper function to delete directory."""
if Path(dir_path).is_dir():
shutil.rmtree(dir_path)
logger.info("Removing directory %s", dir_path)
rmdir(global_save_dir) # remove directory if it exists from previous runs
global_save_dir.mkdir()
logger.info("Creating new directory %s", global_save_dir)
下载数据
对于我们的示例数据,我们将使用一张全切片图像,以及来自 Kather 100k 数据集验证子集的图像块。
wsi_path = global_save_dir / "sample_wsi.svs"
patches_path = global_save_dir / "kather100k-validation-sample.zip"
weights_path = global_save_dir / "resnet18-kather100k.pth"
logger.info("Download has started. Please wait...")
# Downloading and unzip a sample whole-slide image
download_data(
"https://tiatoolbox.dcs.warwick.ac.uk/sample_wsis/TCGA-3L-AA1B-01Z-00-DX1.8923A151-A690-40B7-9E5A-FCBEDFC2394F.svs",
wsi_path,
)
# Download and unzip a sample of the validation set used to train the Kather 100K dataset
download_data(
"https://tiatoolbox.dcs.warwick.ac.uk/datasets/kather100k-validation-sample.zip",
patches_path,
)
with ZipFile(patches_path, "r") as zipfile:
zipfile.extractall(path=global_save_dir)
# Download pretrained model weights for WSI classification using ResNet18 architecture
download_data(
"https://tiatoolbox.dcs.warwick.ac.uk/models/pc/resnet18-kather100k.pth",
weights_path,
)
logger.info("Download is complete.")
读取数据
我们创建了一个补丁列表和一个对应的标签列表。例如,label_list 中的第一个标签将指示 patch_list 中第一个图像补丁的类别。
# Read the patch data and create a list of patches and a list of corresponding labels
dataset_path = global_save_dir / "kather100k-validation-sample"
# Set the path to the dataset
image_ext = ".tif" # file extension of each image
# Obtain the mapping between the label ID and the class name
label_dict = {
"BACK": 0, # Background (empty glass region)
"NORM": 1, # Normal colon mucosa
"DEB": 2, # Debris
"TUM": 3, # Colorectal adenocarcinoma epithelium
"ADI": 4, # Adipose
"MUC": 5, # Mucus
"MUS": 6, # Smooth muscle
"STR": 7, # Cancer-associated stroma
"LYM": 8, # Lymphocytes
}
class_names = list(label_dict.keys())
class_labels = list(label_dict.values())
# Generate a list of patches and generate the label from the filename
patch_list = []
label_list = []
for class_name, label in label_dict.items():
dataset_class_path = dataset_path / class_name
patch_list_single_class = grab_files_from_dir(
dataset_class_path,
file_types="*" + image_ext,
)
patch_list.extend(patch_list_single_class)
label_list.extend([label] * len(patch_list_single_class))
# Show some dataset statistics
plt.bar(class_names, [label_list.count(label) for label in class_labels])
plt.xlabel("Patch types")
plt.ylabel("Number of patches")
# Count the number of examples per class
for class_name, label in label_dict.items():
logger.info(
"Class ID: %d -- Class Name: %s -- Number of images: %d",
label,
class_name,
label_list.count(label),
)
# Overall dataset statistics
logger.info("Total number of patches: %d", (len(patch_list)))

|2023-11-14|13:15:59.299| [INFO] Class ID: 0 -- Class Name: BACK -- Number of images: 211
|2023-11-14|13:15:59.299| [INFO] Class ID: 1 -- Class Name: NORM -- Number of images: 176
|2023-11-14|13:15:59.299| [INFO] Class ID: 2 -- Class Name: DEB -- Number of images: 230
|2023-11-14|13:15:59.299| [INFO] Class ID: 3 -- Class Name: TUM -- Number of images: 286
|2023-11-14|13:15:59.299| [INFO] Class ID: 4 -- Class Name: ADI -- Number of images: 208
|2023-11-14|13:15:59.299| [INFO] Class ID: 5 -- Class Name: MUC -- Number of images: 178
|2023-11-14|13:15:59.299| [INFO] Class ID: 6 -- Class Name: MUS -- Number of images: 270
|2023-11-14|13:15:59.299| [INFO] Class ID: 7 -- Class Name: STR -- Number of images: 209
|2023-11-14|13:15:59.299| [INFO] Class ID: 8 -- Class Name: LYM -- Number of images: 232
|2023-11-14|13:15:59.299| [INFO] Total number of patches: 2000
正如您所见,对于这个补丁数据集,我们有9个类别/标签,ID从0到8,并附有相关的类别名称,这些名称描述了补丁中的主要组织类型:
-
BACK ⟶ 背景(空白玻璃区域)
-
LYM ⟶ 淋巴细胞
-
NORM ⟶ 正常结肠黏膜
-
DEB ⟶ 碎片
-
MUS ⟶ 平滑肌
-
STR ⟶ 癌症相关间质
-
ADI ⟶ 脂肪
-
MUC ⟶ 黏液
-
TUM ⟶ 结直肠腺癌上皮
分类图像块
我们首先演示如何使用 patch 模式获取数字切片中每个区块的预测结果,然后使用 wsi 模式处理整个大切片。
定义 PatchPredictor 模型
PatchPredictor 类运行一个基于 CNN 的分类器,该分类器使用 PyTorch 编写。
-
model可以是任何经过训练的 PyTorch 模型,但需遵循tiatoolbox.models.abc.ModelABC(文档) <https://tia-toolbox.readthedocs.io/en/latest/_autosummary/tiatoolbox.models.models_abc.ModelABC.html>`__ 类结构。有关更多信息,请参考 我们关于高级模型技术的示例笔记本。为了加载自定义模型,您需要编写一个小的预处理函数,如preproc_func(img),以确保输入张量符合加载网络的格式要求。 -
或者,您可以将
pretrained_model作为字符串参数传递。这指定了执行预测的 CNN 模型,它必须是 这里 列出的模型之一。命令将如下所示:predictor = PatchPredictor(pretrained_model='resnet18-kather100k', pretrained_weights=weights_path, batch_size=32)。 -
pretrained_weights:使用pretrained_model时,默认情况下也会下载相应的预训练权重。您可以通过pretrained_weight参数覆盖默认值,使用自己的权重集。 -
batch_size:每次输入模型的图像数量。此参数的值越高,所需的(GPU)内存容量越大。
# Importing a pretrained PyTorch model from TIAToolbox
predictor = PatchPredictor(pretrained_model='resnet18-kather100k', batch_size=32)
# Users can load any PyTorch model architecture instead using the following script
model = vanilla.CNNModel(backbone="resnet18", num_classes=9) # Importing model from torchvision.models.resnet18
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(weights_path, map_location="cpu", weights_only=True), strict=True)
defpreproc_func(img):
img = PIL.Image.fromarray(img)
img = transforms.ToTensor()(img)
return img.permute(1, 2, 0)
model.preproc_func = preproc_func
predictor = PatchPredictor(model=model, batch_size=32)
预测图像块标签
我们创建一个预测器对象,然后使用 patch 模式调用 predict 方法。接着计算分类准确率和混淆矩阵。
with suppress_console_output():
output = predictor.predict(imgs=patch_list, mode="patch", on_gpu=ON_GPU)
acc = accuracy_score(label_list, output["predictions"])
logger.info("Classification accuracy: %f", acc)
# Creating and visualizing the confusion matrix for patch classification results
conf = confusion_matrix(label_list, output["predictions"], normalize="true")
df_cm = pd.DataFrame(conf, index=class_names, columns=class_names)
df_cm
|2023-11-14|13:16:03.215| [INFO] Classification accuracy: 0.993000
| BACK | NORM | DEB | TUM | ADI | MUC | MUS | STR | LYM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BACK | 1.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.00000 |
| NORM | 0.000000 | 0.988636 | 0.000000 | 0.011364 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.00000 |
| DEB | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.991304 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.008696 | 0.00000 |
| TUM | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.996503 | 0.000000 | 0.003497 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.00000 |
| ADI | 0.004808 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.990385 | 0.000000 | 0.004808 | 0.000000 | 0.00000 |
| MUC | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.988764 | 0.000000 | 0.011236 | 0.00000 |
| MUS | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.996296 | 0.003704 | 0.00000 |
| STR | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.004785 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.004785 | 0.004785 | 0.985646 | 0.00000 |
| LYM | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.004310 | 0.99569 |
预测整张切片的标签
我们现在介绍 IOPatchPredictorConfig,这是一个用于指定模型预测引擎的图像读取和预测写入配置的类。这是为了告知分类器应该读取哪个层次的 WSI 金字塔,处理数据并生成输出。
IOPatchPredictorConfig 的参数定义如下:
-
input_resolutions: 一个字典形式的列表,用于指定每个输入的分辨率。列表元素的顺序必须与目标model.forward()中的输入顺序一致。如果您的模型只接受一个输入,您只需提供一个字典,指定'units'和'resolution'。请注意,TIAToolbox 支持具有多个输入的模型。有关单位和分辨率的更多信息,请参阅 TIAToolbox 文档。 -
patch_input_shape: 最大输入的形状,格式为 (高度, 宽度)。 -
stride_shape: 在提取补丁过程中,两个连续补丁之间的步幅(步长)大小。如果用户将stride_shape设置为与patch_input_shape相同,补丁将无重叠地提取和处理。
wsi_ioconfig = IOPatchPredictorConfig(
input_resolutions=[{"units": "mpp", "resolution": 0.5}],
patch_input_shape=[224, 224],
stride_shape=[224, 224],
)
predict 方法将 CNN 应用于输入图像块并获取结果。以下是参数及其描述:
-
mode: 要处理的输入类型。根据您的应用选择patch、tile或wsi。 -
imgs: 输入列表,应为输入图块或 WSI 的路径列表。 -
return_probabilities: 设置为 True 以获取输入图块的每类概率以及预测标签。如果您希望合并预测以生成tile或wsi模式的预测图,可以设置return_probabilities=True。 -
ioconfig: 使用IOPatchPredictorConfig类设置 IO 配置信息。 -
resolution和unit(未在下方显示):这些参数指定我们计划从中提取图块的 WSI 级别的分辨率或每像素微米数,可以代替ioconfig使用。在这里,我们将 WSI 级别指定为'baseline',这相当于级别 0。通常,这是最高分辨率的级别。在此特定情况下,图像只有一个级别。更多信息请参阅文档。 -
masks: 与imgs列表中 WSI 的掩码对应的路径列表。这些掩码指定了我们希望从中提取图块的原始 WSI 区域。如果某个特定 WSI 的掩码指定为None,则预测该 WSI 的所有图块(包括背景区域)的标签。这可能会导致不必要的计算。 -
merge_predictions: 如果需要生成图块分类结果的 2D 图,可以设置此参数为True。然而,对于大型 WSI,这将需要大量可用内存。另一种(默认)解决方案是将merge_predictions=False,然后使用merge_predictions函数生成 2D 预测图,稍后您将看到。
由于我们使用的是大型 WSI,图像块提取和预测过程可能需要一些时间(如果您有支持 Cuda 的 GPU 并且安装了 PyTorch+Cuda,请确保将 ON_GPU=True 设置为启用 GPU 加速)。
with suppress_console_output():
wsi_output = predictor.predict(
imgs=[wsi_path],
masks=None,
mode="wsi",
merge_predictions=False,
ioconfig=wsi_ioconfig,
return_probabilities=True,
save_dir=global_save_dir / "wsi_predictions",
on_gpu=ON_GPU,
)
我们通过可视化 wsi_output 来观察预测模型在整个切片图像上的表现。首先需要合并每个图块的预测输出,然后将它们作为覆盖层可视化在原始图像上。与之前一样,使用 merge_predictions 方法来合并图块预测。在这里,我们设置参数 resolution=1.25, units='power',以生成在 1.25 倍放大倍率下的预测图。如果您希望生成更高/更低分辨率(更大/更小)的预测图,需要相应地调整这些参数。当预测合并完成后,使用 overlay_patch_prediction 函数将预测图覆盖在 WSI 缩略图上,该缩略图应在预测合并时使用的分辨率下提取。
overview_resolution = (
4 # the resolution in which we desire to merge and visualize the patch predictions
)
# the unit of the `resolution` parameter. Can be "power", "level", "mpp", or "baseline"
overview_unit = "mpp"
wsi = WSIReader.open(wsi_path)
wsi_overview = wsi.slide_thumbnail(resolution=overview_resolution, units=overview_unit)
plt.figure(), plt.imshow(wsi_overview)
plt.axis("off")

将预测图叠加在此图像上得到:
# Visualization of whole-slide image patch-level prediction
# first set up a label to color mapping
label_color_dict = {}
label_color_dict[0] = ("empty", (0, 0, 0))
colors = cm.get_cmap("Set1").colors
for class_name, label in label_dict.items():
label_color_dict[label + 1] = (class_name, 255 * np.array(colors[label]))
pred_map = predictor.merge_predictions(
wsi_path,
wsi_output[0],
resolution=overview_resolution,
units=overview_unit,
)
overlay = overlay_prediction_mask(
wsi_overview,
pred_map,
alpha=0.5,
label_info=label_color_dict,
return_ax=True,
)
plt.show()

使用病理学特定模型进行特征提取
在本节中,我们将展示如何使用 TIAToolbox 提供的 WSI 推理引擎,从存在于 TIAToolbox 之外的预训练 PyTorch 模型中提取特征。为了说明这一点,我们将使用 HistoEncoder,这是一个特定于计算病理学的模型,该模型通过自监督的方式进行训练,用于从组织学图像中提取特征。该模型已在此处提供:
‘HistoEncoder: Foundation models for digital pathology’ (https://github.com/jopo666/HistoEncoder) by Pohjonen, Joona 和赫尔辛基大学的团队。
我们将绘制特征图的 umap 降维到 3D (RGB) 的图,以可视化这些特征如何捕捉上述某些组织类型之间的差异。
# Import some extra modules
importhistoencoder.functionalasF
importtorch.nnasnn
fromtiatoolbox.models.engine.semantic_segmentorimport DeepFeatureExtractor, IOSegmentorConfig
fromtiatoolbox.models.models_abcimport ModelABC
importumap
TIAToolbox 定义了一个 ModelABC,它是一个继承自 PyTorch nn.Module 的类,并指定了模型应具备的结构,以便在 TIAToolbox 推理引擎中使用。histoencoder 模型并未遵循此结构,因此我们需要将其封装在一个类中,使得该类的输出和方法符合 TIAToolbox 引擎的预期。
classHistoEncWrapper(ModelABC):
"""Wrapper for HistoEnc model that conforms to tiatoolbox ModelABC interface."""
def__init__(self: HistoEncWrapper, encoder) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.feat_extract = encoder
defforward(self: HistoEncWrapper, imgs: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
"""Pass input data through the model.
Args:
imgs (torch.Tensor):
Model input.
"""
out = F.extract_features(self.feat_extract, imgs, num_blocks=2, avg_pool=True)
return out
@staticmethod
definfer_batch(
model: nn.Module,
batch_data: torch.Tensor,
*,
on_gpu: bool,
) -> list[np.ndarray]:
"""Run inference on an input batch.
Contains logic for forward operation as well as i/o aggregation.
Args:
model (nn.Module):
PyTorch defined model.
batch_data (torch.Tensor):
A batch of data generated by
`torch.utils.data.DataLoader`.
on_gpu (bool):
Whether to run inference on a GPU.
"""
img_patches_device = batch_data.to('cuda') if on_gpu else batch_data
model.eval()
# Do not compute the gradient (not training)
with torch.inference_mode():
output = model(img_patches_device)
return [output.cpu().numpy()]
现在我们有了封装器,我们将创建特征提取模型并实例化一个 DeepFeatureExtractor,以便能够在全视野数字切片(WSI)上使用该模型。我们将使用与之前相同的 WSI,但这次我们将使用 HistoEncoder 模型从 WSI 的补丁中提取特征,而不是为每个补丁预测某个标签。
# create the model
encoder = F.create_encoder("prostate_medium")
model = HistoEncWrapper(encoder)
# set the pre-processing function
norm=transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.662, 0.446, 0.605],std=[0.169, 0.190, 0.155])
trans = [
transforms.ToTensor(),
norm,
]
model.preproc_func = transforms.Compose(trans)
wsi_ioconfig = IOSegmentorConfig(
input_resolutions=[{"units": "mpp", "resolution": 0.5}],
patch_input_shape=[224, 224],
output_resolutions=[{"units": "mpp", "resolution": 0.5}],
patch_output_shape=[224, 224],
stride_shape=[224, 224],
)
当我们创建 DeepFeatureExtractor 时,我们将传入 auto_generate_mask=True 参数。这将自动使用 Otsu 阈值法生成组织区域的掩码,以便提取器仅处理包含组织的图像块。
# create the feature extractor and run it on the WSI
extractor = DeepFeatureExtractor(model=model, auto_generate_mask=True, batch_size=32, num_loader_workers=4, num_postproc_workers=4)
with suppress_console_output():
out = extractor.predict(imgs=[wsi_path], mode="wsi", ioconfig=wsi_ioconfig, save_dir=global_save_dir / "wsi_features",)
这些特征可用于训练下游模型,但为了直观理解这些特征所代表的含义,我们将使用UMAP降维技术将其在RGB空间中可视化。被标记为相似颜色的点应该具有相似的特征,因此我们可以在WSI缩略图上叠加UMAP降维结果,检查这些特征是否自然地分离到不同的组织区域。我们将在接下来的代码单元中将其与之前的分块预测图一起绘制,以比较这些特征与分块预测的结果。
# First we define a function to calculate the umap reduction
defumap_reducer(x, dims=3, nns=10):
"""UMAP reduction of the input data."""
reducer = umap.UMAP(n_neighbors=nns, n_components=dims, metric="manhattan", spread=0.5, random_state=2)
reduced = reducer.fit_transform(x)
reduced -= reduced.min(axis=0)
reduced /= reduced.max(axis=0)
return reduced
# load the features output by our feature extractor
pos = np.load(global_save_dir / "wsi_features" / "0.position.npy")
feats = np.load(global_save_dir / "wsi_features" / "0.features.0.npy")
pos = pos / 8 # as we extracted at 0.5mpp, and we are overlaying on a thumbnail at 4mpp
# reduce the features into 3 dimensional (rgb) space
reduced = umap_reducer(feats)
# plot the prediction map the classifier again
overlay = overlay_prediction_mask(
wsi_overview,
pred_map,
alpha=0.5,
label_info=label_color_dict,
return_ax=True,
)
# plot the feature map reduction
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(wsi_overview)
plt.scatter(pos[:,0], pos[:,1], c=reduced, s=1, alpha=0.5)
plt.axis("off")
plt.title("UMAP reduction of HistoEnc features")
plt.show()
我们发现,来自我们 patch-level 预测器的预测图与来自自监督特征编码器的特征图,捕获了关于 WSI 中组织类型的相似信息。这是一个很好的验证,表明我们的模型正在按预期工作。这也表明,HistoEncoder 模型提取的特征正在捕捉组织类型之间的差异,因此它们编码了组织学相关的信息。
下一步
在本笔记本中,我们展示了如何使用 PatchPredictor 和 DeepFeatureExtractor 类及其 predict 方法来预测大切片和WSI(全片扫描图像)的标签或提取特征。我们介绍了 merge_predictions 和 overlay_prediction_mask 辅助函数,它们用于合并切片预测输出,并将生成的预测地图作为输入图像/WSI的叠加层进行可视化。
所有这些过程都在TIAToolbox中进行,我们可以按照示例代码轻松地将各个部分组合在一起。请确保正确设置输入和选项。我们鼓励您进一步研究更改 predict 函数参数对预测输出的影响。我们演示了如何在TIAToolbox框架中使用您自己的预训练模型或研究社区提供的特定任务模型,即使模型结构未在TIAToolbox模型类中定义,也可以对大型WSI进行推理。
您可以通过以下资源了解更多信息:


